What Is a Neet and How Is Gaming Associated With It?
It’s easy to dismiss NEET as just another acronym used to save time when messaging, like LMK, BRB, or GTG. But unlike those harmless slang terms, NEET is more serious and less understood. In our gamer and parent forums, NEET causes confusion whenever it’s mentioned. We’re asked questions like:
- What is the meaning of NEETs?
- What does NEET stand for?
- What does NEET mean in slang?
- What is Gen Z NEET?
In this article, we explain what the acronym means, what causes people to become NEETs, and how gaming can be associated with it.
NEET meaning and global prevalence

NEET is an acronym used to describe young people aged 15-24 who are not in education, employment, or training. It’s not just a slang term, but an indicator recognized by the World Health Organization 1 1. https://www.who.int/data/gho/indicator-metadata-registry/imr-details/proportion-of-young-people-aged-15-24-years-not-in-education-employment-or-training × . In fact, NEET was included as a target on the UN’s 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development as a Sustainable Development Goal (SDG): “By 2020, substantially reduce the proportion of youth not in employment, education, or training.” 2 2. https://sdgs.un.org/goals/goal8#overview ×
But the 2024 SDG report found that NEET rates across the world are still high 3 3. https://unstats.un.org/sdgs/report/2024/The-Sustainable-Development-Goals-Report-2024.pdf × :
- Around 269 million young people globally are NEET.
- More than one in five youths worldwide (21.7%) are NEET.
- Young women are more than twice as likely as young men to be NEET.
- Only 36 of the 87 countries included in the report had implemented a national strategy for youth employment.
What causes people to become NEETs?
There are a number of factors that can contribute to young people being NEETs:
Disengagement with education
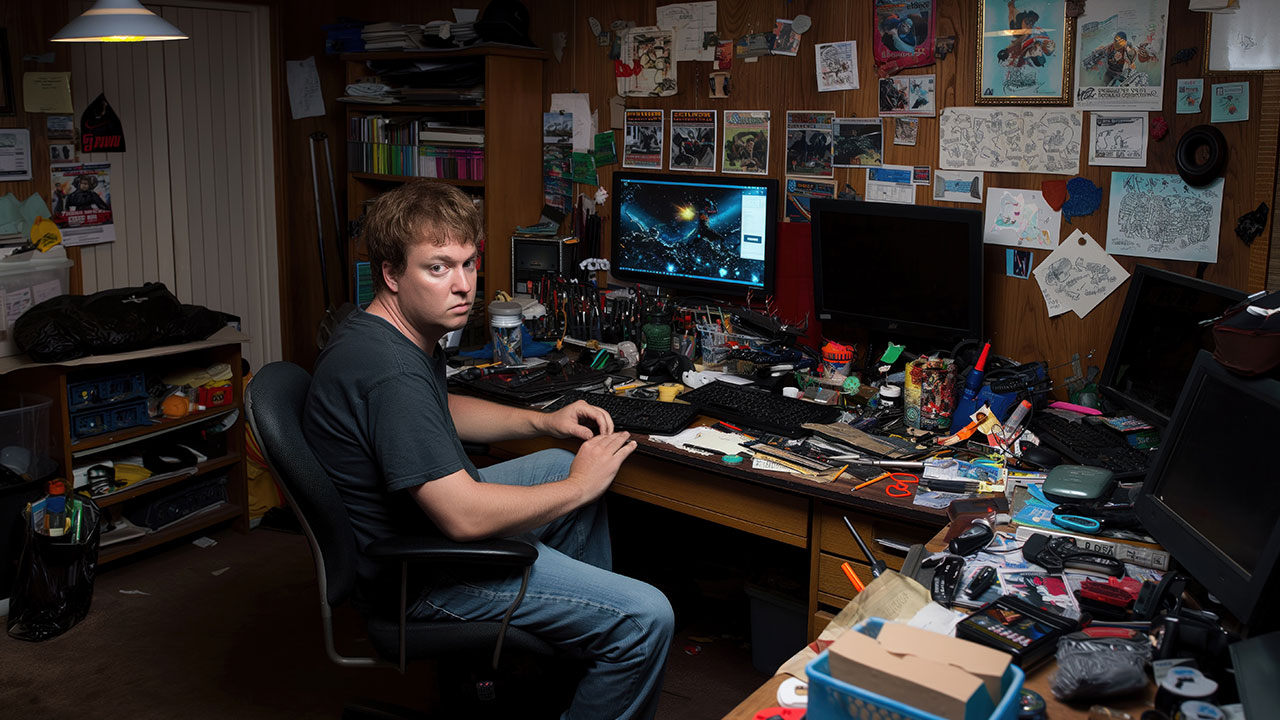
Young people can become disconnected from the education system through poor attendance, suspension, or exclusion, which means they fall behind their peers in the classroom. This can make them even less inclined to go to school, especially if there’s low parental involvement. Other factors that may cause disengagement from education include bullying, excessive gaming at school, and special educational needs or mental health problems that the school doesn’t have the resources to support.
Lack of skills and qualifications
If a young person leaves school with no skills or qualifications, it can be very difficult to find a job, training opportunity, or even unpaid work experience. Other factors that can impede their access to employment include inadequate career advice and a lack of support with the job application and interview process. In some cases, such as those with video game addiction, continuing to play video games can be more appealing than working a job.
Health and well-being
Mental health issues like depression and anxiety can impact a young person’s ability to attend school, training, or work. And situations they may encounter in education or employment can worsen their mental health. Low self-esteem or lack of self-confidence are also factors that sometimes stop youth from moving on with their lives. And having a disability can be an ongoing challenge if the necessary support or adjustments are not in place at school or work.
Family circumstances
NEETs are often influenced by their family circumstances and are more likely to be unemployed if their parents are unemployed. People from poorer backgrounds also have fewer opportunities to progress in life than their wealthier peers. Other factors, such as caring responsibilities or teenage pregnancy, can also be barriers to education and the workplace for those affected.
Local NEET rate
Gender-based restrictions on schooling and other local factors can increase the NEET rate in certain regions. For example, in Central and Southern Asia, almost half of young women are NEET compared to only 12.3% of young men. And this disparity is similar in Western Asia and Northern Africa.
Lifestyle choices
Certain unhealthy lifestyle choices can make it difficult for young people to engage with education or hold down a job. These include substance use disorders, compulsive gambling, alcohol misuse, and video game addiction. The impact of excessive gaming on job prospects is reflected in the Game Quitters community, which is predominantly males aged 18-32. Only 35% of members are in full-time employment—44% are unemployed, and 21% work part-time or casually—and 60% of them earn less than $500 per month.
How is gaming associated with NEETs?
So, what does a NEET do all day? Most young people in this position are unable to support themselves financially, which can make it difficult to pursue hobbies or have a social life without parental help. And family members can feel frustrated if their offspring continues to live in the family home with no prospect of moving out and eventually may stop enabling their adult child.
So NEETS often turn to the TV, internet, or gaming for ‘free’ entertainment. However, an over-reliance on screens can make their situation worse. For example, by escaping into video games, the young person avoids real-life responsibilities and gets further behind their peers, so they feel even less inclined to re-engage in the world.
With so much time on their hands, it’s easy for NEETs to play more and more frequently, until gaming is no longer a choice—it becomes a compulsion. This is because their brains become hijacked by dopamine, and they need more and more of this feel-good neurotransmitter to get the same rush of pleasure when gaming.
If you’re concerned that you or someone you care about may be gaming problematically, check out the signs of video game addiction and take our short quiz to decide if you (or they) need support.
Need help?
Do you feel like you’re being left behind while all your friends are getting on with their lives? If you or a loved one are NEET because gaming is consuming every waking hour, we can help.
It is possible to get your gaming under control so you can return to school or college, or find a job or training opportunity. Tens of thousands of people from all over the world have been able to stop playing video games compulsively, and you can too.
Book a Gameplan Call, so we can see if you’re a good fit for one of our specialist coaching programs. We’re also experienced at helping families of gamers who are in denial.
We’ll discuss your current situation to understand why you’re NEET and explain how to get your gameplay under control in order to become more productive, confident, and motivated.