How Gaming Affects the Brain
Table of Contents
There is an ongoing debate about the effects of video games on the brain. Some studies suggest that video games help learning and build skills, while others have found they can make players more violent or aggressive. It is evident that the impact of video games on the brain is not clear-cut; they can have both beneficial and harmful effects.
This article examines how video games can change your brain and looks at the positive and negative consequences of gaming. We also share tips on what to do if video games are starting to cause problems.
The psychology of gaming
Video games are deliberately designed to be addictive. The gaming industry employs cognitive psychologists, reward psychologists, and computer science and human behavioral scientists as user experience (UX) designers. They apply their knowledge of attention, perception, memory, emotion, reward and learning principles, and psychological vulnerabilities in game design. Every second of color, light, sound, purpose, task, instruction and experience within video games is carefully crafted to keep players (brains) gaming for as long as possible and spending money on in-game purchases.
Professor David Hodgins of the University of Calgary, an addictive behaviors and clinical psychology researcher says “we know that young people are overly involved in gaming and gambling. One common game design feature is intermittent reinforcement, which means there are a lot of rewards but the rewards are unpredictable, so people pursue the rewards in a constant fashion. This is a concept we’ve known since the 1950s.”
What gaming does to the brain
Parents of gamers are sometimes concerned about video games and brain development. They ask us questions like:
- “Does too much gaming rot your brain?”
- “Is there a difference between gamer brain vs normal brain?”
Video games can impact the brain in several ways and certain changes are more obvious than others. Here are some of the most common effects gaming can have on the cognition, brain structure and function:
Gaming activates dopamine – the brain’s reward system

Dopamine is a feel-good neurotransmitter that’s part of the brain’s reward system. Whenever the brain is expecting a reward from a certain activity, it starts producing dopamine which makes us feel good. This motivates us to repeat the behavior to experience the same rush of pleasure. So, do video games release dopamine?
If gaming is balanced with other hobbies and interests, the brain will receive small doses of dopamine and players will feel happy and motivated. This is a simple effect of video games on the brain. But long and frequent gaming sessions can release such huge doses of dopamine over and over, that the brain will try to stay in balance by shutting down its ability to get dopamine. In response, players often start to play more to try to experience the same thrill, but the brain will compensate by shutting down even more of its ability to get dopamine. Eventually, this cycle will mean the brain doesn’t produce enough dopamine and it will become dopamine deficient.
What are the symptoms of dopamine deficiency? Those who game excessively may start to wonder: “Do video games cause brain fog?” or “Do video games rot your brain?” It is common for sufferers to feel tired, irritable and anxious, and many people struggle to concentrate. Things that used to be interesting seem pointless but it’s gaming that is changing their brains so that nothing feels fun or exciting. They start to game more, not always because they want to play, but to relieve the uncomfortable feelings from having low dopamine. And the vicious circle continues.
It’s related to a biological process called tolerance and sugar is a good example of how this works. A little bit of sugar once in a while is ok, but the more you have the more you want. You end up developing a tolerance to sugar, needing increasing amounts to experience the same effects. This is the same for gaming. The more people play, the more their brains become less sensitive to the effects of dopamine, and it takes more and more dopamine to feel that same pleasure and excitement.
Gaming can cause a fight-or-flight response
Our natural fight-or-flight response is designed to protect us when we sense danger. The body releases hormones that increase our heart and breathing rates and gets our muscles ready to respond. In some situations, it can be a lifesaver by helping us stay focused, alert and able to react quickly.
However, there is a point at which the fight-or-flight response stops being beneficial and starts causing problems. This can happen when playing violent video games. Over time, the brain may think the threats and attacks are real and the game is actually a battle. This can cause the player to react angrily and aggressively. So, if you have ever wondered how violent video games affect the brain differently, it is the fight-or-flight amygdala that has taken over so the player cannot access the logical part of their brain.
Gaming lowers activity in the prefrontal cortex of the developing brain
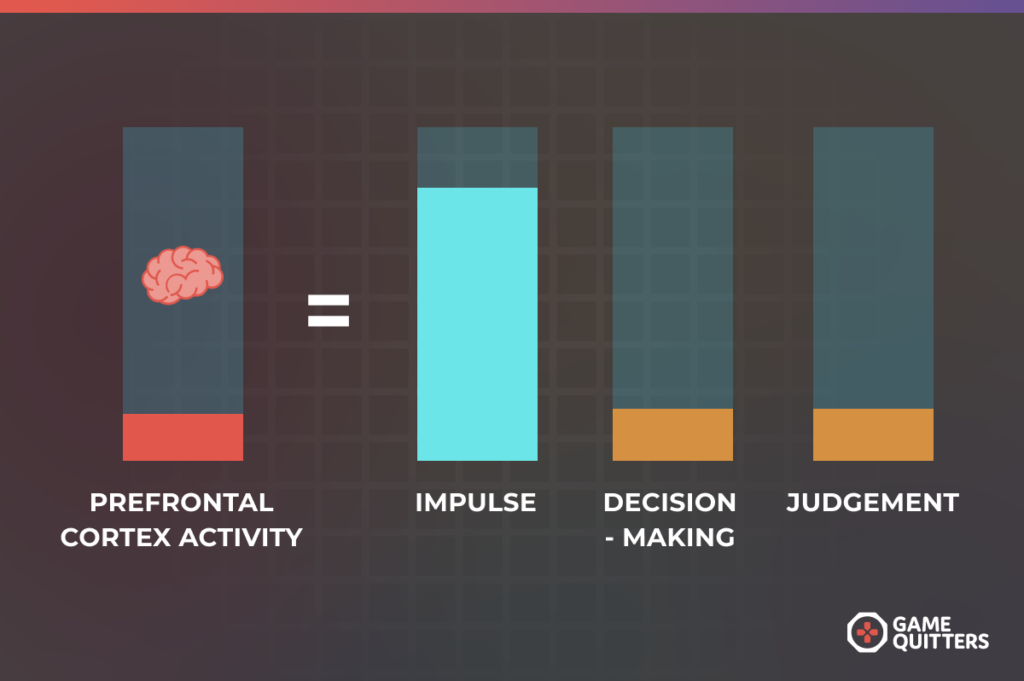
The prefrontal cortex of the brain – which is responsible for decision-making, judgement and self-control – does not fully develop until the age of 25. This can make young gamers less able to weigh up the pros and cons of immediate rewards, like another few hours spent gaming, against longer-term goals such as revising for their math test next week. This may also explain why some young gamers neglect their basic needs such as food, sleep, exercise and personal hygiene in order to continue playing video games.
Researchers have found that violent games, in particular, can lower activity in developing brains. One study reported that young male gamers who spent many hours playing a violent video game for two weeks had lower activity in important brain areas when trying to control their behavior, compared to adolescents who played no video games over that period. Another study of youth gamers found that playing violent video games for just 30 minutes, immediately lowered activity in the prefrontal cortex compared to the brains of those who played non-violent video games.
Gaming can trigger the release of adrenaline and cortisol
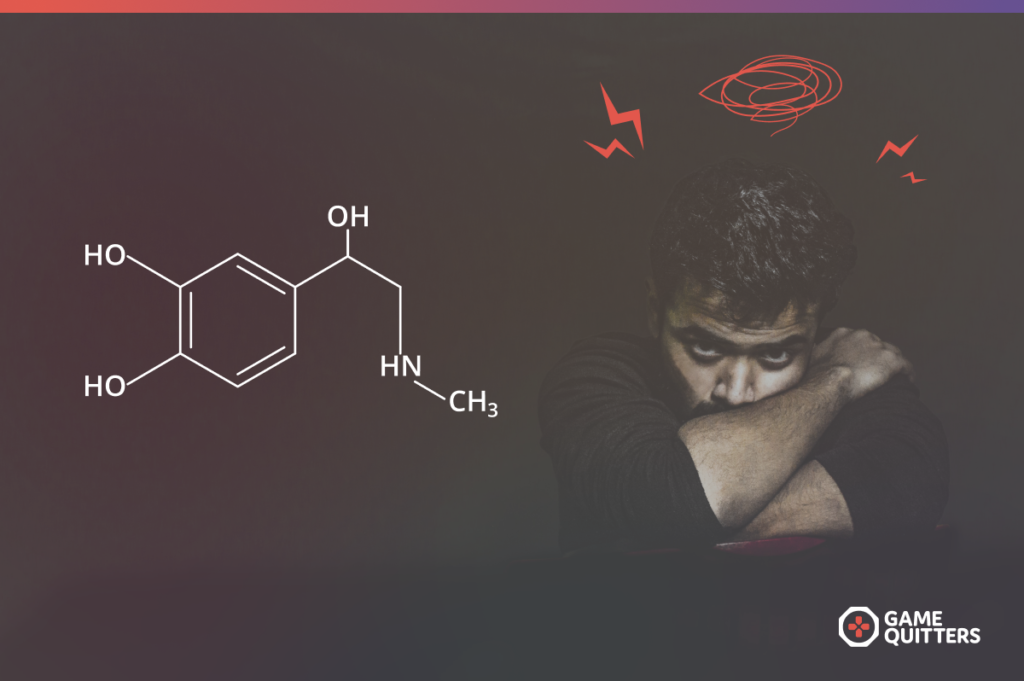
Many video games are action packed and intense, and this excitement triggers the production of adrenalin. It’s a natural reaction to help us react faster to situations of perceived danger – such as the risk of dying in a shooting game such as Valorant, Counter-Strike or Call of Duty. When excess adrenaline is released into the bloodstream, it makes the heart pump harder than usual. This increases our blood pressure, heart rate and breathing rate. After a while, the blood shifts to the limbic system, the part of the brain involved in our emotional and behavioral responses, which can cause brain fog, sometimes called becoming a game zombie.
Gaming can also increase the release of cortisol (known as the stress hormone) in response to perceived threats. If the stress hormone is constantly active due to excessive gaming, it may cause the brain’s neurotransmitters – like serotonin – to stop functioning correctly. This can affect our mood, potentially causing depression; blood sugar, which can lead to the over-consumption of junk food, and sleep quality because it becomes more difficult to fall asleep and stay asleep. This is why there is a debate about whether or not gaming reduces stress.
Does gaming rot the brain?
Gaming does not rot the brain. When video games are played for fun as part of a healthy range of activities, there is generally no cause for concern. Most of the negative effects of video games are due to excessive use or underlying issues:
- Physical health risks including repetitive strain injury, headaches, back and neck problems, obesity and heart-related issues
- Poor personal hygiene, laziness
- Insomnia and other sleep-related problems
- Mental health conditions including anxiety, stress and depression
- Mood swings such as irritability, anger, aggression and violence
- Family conflict and relationship issues
- Lack of motivation, concentration and energy
- Cognitive biases that affect decision-making skills and problem-solving abilities
- Loneliness and social disconnection
- Exposure to online toxicity and harassment
- Poor academic performance and missed career opportunities
- Loss of interest in other activities.
For a small percentage of players, the negative effects of gaming can include addiction. Take our video game addiction test to see if your gaming habits are potentially problematic.
Positive effects of gaming on brain development

When played in moderation, video games can have multiple benefits on the brain:
Video games can enhance attention
Research has found that areas of the brain involved in attention are more efficient in people who play video games who are able keep their attention focused on demanding tasks. 1 1. Frontiers. "Video games can change your brain: Studies investigating how playing video games can affect the brain have shown that they can cause changes in many brain regions." ×
Video games can increase intelligence
Researchers at the Karolinska Institutet in Stockholm and Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam found that US children who spent an above-average amount of time playing video games increased their intelligence by approximately 2.5 IQ points more than the average. However, watching TV and engaging with social media had no significant impact on their cognitive abilities. 2 2. Video games can help boost children’s intelligence</a< ×
Video games can improve memory
Gaming can have long-lasting benefits for memory. A study by the Universitat Oberta de Catalunya in Barcelona using Nintendo’s Super Mario 64 found that playing video games as a child can improve a person’s working memory years afterwards. 3 3. Video gaming as a child related to improvements in memory ×
Video games can boost learning
Playing action video games has been found to improve learning capabilities. Research by the University of Rochester reported that our brains are constantly building ‘templates’ of the world to make better predictions and playing action video games enables gamers to produce better templates than non-gamers. 4 4. Playing action video games can boost learning ×
Video games can enhance problem-solving skills
Gaming teaches players to keep trying to reach the next level, complete the next quest or get to the top of the leader board. It is a safe space to fail and if they don’t initially succeed, they can try different strategies to achieve their goal. A 2013 study found the more that adolescents playing strategic video games, the better their problem-solving skills and academic grades were the following year. 5 5. More Than Just Fun and Games: The Longitudinal Relationships Between Strategic Video Games, Self-Reported Problem Solving Skills, and Academic Grades ×
Video games can encourage creativity
Sandbox games, like Minecraft, Roblox, Stardew Valley and SimCity, give players the creative freedom to build and explore different worlds. This link between video games and creativity is backed by research from Iowa State University. It found that playing Minecraft without instruction improved participants’ creativity more than watching TV or playing a race car video game. 6 6. Want to boost creativity? Try playing Minecraft Date: ×
Best games for your brain

There are various puzzles and games for the brain designed to sharpen the memory. These games may also be better alternatives than immersive multiplayer video games.
Sudoku
This logic-based number puzzle improves memory and concentration. There are different levels of difficulty so you can find the right level of challenge.
Wordle
Wordle provides a small hit of dopamine (only one puzzle is released each day), uses problem-solving skills and can provide social interaction if you share your result on social media.
Jigsaws
Jigsaw puzzles use both the left and right-hand side of your brain. As well improving problem-solving skills and visual-spatial reasoning, they are a great stress reliever.
Chess
Playing chess on a board rather than online is a good way to have a screen break. It is proven to be an excellent cognitive exercise that boosts logical reasoning and memory.
Crossword puzzles
Regularly completing crosswords can help improve focus and attention. A study in the Journal of the International Neuropsychology Society found that crosswords may delay the onset of memory loss in people with dementia. 7 7. Association of Crossword Puzzle Participation with Memory Decline in Persons Who Develop Dementia ×
By choosing the right games to play you can gain benefits from gaming on your brain instead of negative ones.
How to reset the gamer brain

When you find yourself or someone you love struggling with excessive gaming or social media use, you may wonder how to reset their brain back to normal. The key may be simpler than you think.
As described above, the dopamine theory of addiction states that addictions increase dopamine to an extent that once the stimulus is removed, our body may be unable to replicate the same amount of dopamine naturally. Therefore, the key towards overcoming an addiction is to restore the ability of the body to create dopamine through natural means, without the stimulus someone is addicted to.
For example, for someone who has what is now described as TikTok brain, they may benefit from a dopamine detox.
A dopamine detox involves abstaining from all addictive activities that raise your levels of dopamine higher than natural. A digital detox includes abstaining from activities such as social media, video games, smartphones and gambling. You’ll abstain from instant hits of dopamine and replace them with healthier activities that produce dopamine such as exercise, time in nature and face-to-face interactions.
For a dopamine detox to be most effective, a recommended time of 90 days works best, however benefits can be found in shorter detox periods as well. For more information, read our guide on how to do a dopamine detox.
If you are concerned about your gaming habits, or you think a loved one may have gaming problems, we can help.
- Our Reclaim program is specifically designed to help families reduce conflict, manage problematic gaming and learn how to control gaming and screen time.
- Our Respawn program helps gamers detox from gaming and get their live back on track.
- Book a Gameplan call to discuss your situation. Limited spots are available.
Footnotes
- Frontiers. "Video games can change your brain: Studies investigating how playing video games can affect the brain have shown that they can cause changes in many brain regions." ↩
- Video games can help boost children’s intelligence</a< ↩
- Video gaming as a child related to improvements in memory ↩
- Playing action video games can boost learning ↩
- More Than Just Fun and Games: The Longitudinal Relationships Between Strategic Video Games, Self-Reported Problem Solving Skills, and Academic Grades ↩
- Want to boost creativity? Try playing Minecraft Date: ↩
- Association of Crossword Puzzle Participation with Memory Decline in Persons Who Develop Dementia ↩